Insert the missing part of the command to check which version of Git (if any) is installed.
- git —versoin
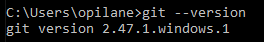
Initialize Git on the current folder:
- git init
Set the user name for the current repository to «w3schools-test»:
- git config user.name «w3schools-test»

Check the status of the Git:
- git status
Add index.html to the Staging Enviornment:
- git add
index.html
Stage all new, modified, and deleted files. Use the shorthand command:
- git add -A
Commit the changes to the current repository with the message «First release!»
- git commit -m «First release!»
Check the compact version of the status for repository:
- git status —short
Commit the updated files directly, skipping the staging environment:
- git commit -a -m «New line added»
View the history of commits for the repository:
- git log
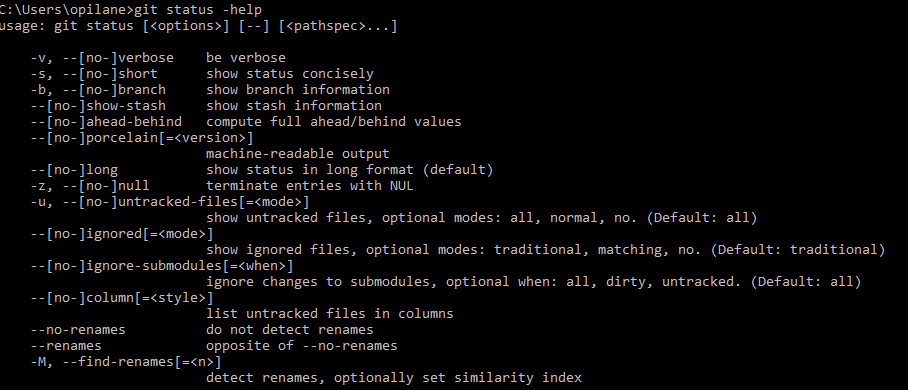
Show the possible options for the status command in command line:
- git status -help
Show all git possible commands in command line:
- git help —all
Create a new branch called hello-world-images:
- git branch hello-world-images
List the existing branches:
- git branch
Move to the hello-world-images branch:
- git checkout
hello-world-images
Create, and move to a new branch with the name hello-you:
- git checkout -b
Merge the hello-you branch with the current branch:
- git merge hello-you
Remove the hello-you branch from the local repository:
- git branch -d hello-you
Add a remote repository as an origin:
- git remote add origin https://github.com/x/y.git
pull is a combination of:
- fetch and then merge
Get all the change history of the origin for this branch:
- git fetch origin
Merge the current branch with the branch master, on origin:
- git merge origin/master
Update the current branch from its origin using a single command:
- git pull origin
push the current branch to its default remote origin:
- git push origin
List all local and remote branches of the current Git.
- git branch -a
List only remote branches of the current Git.
- git branch -r
Clone the repository: https://abc.com/x/y.git to your local Git:
- git clone https://abc.com/x/y.git
Clone the repository https://abc.com/x/y.git to a folder named «newlife«:
- git clone https://abc.com/x/y.git newlife
Rename the origin remote to upstream:
- git remote rename origin
upstream
In .gitignore add a line to ignore all .temp files:
- *.temp
In .gitignore add a line to ignore all files in any directory named temp:
- temp/
In .gitignore add a single line to ignore all files named temp1.log, temp2.log, and temp3.log:
- temp?.log
In .gitignore, ignore all .log files, except main.log:
- *.log
- !main.log’
Add a new remote named ssh-origin connecting to x/y.git on abc.com using SSH:
- git remote add ssh-origin git@abc.com:x/y.git
Replace the remote URL for origin with x/y.git on abc.com using SSH:
- git remoat set-url origin git@abc.com:x/y.git